punjabtechnicaluniversity.blogspot.in
Dec 2013 Paper 3
01.
If the primal Linear Programming problem has unbounded
solution, then it’s dual problem will have
(A) feasible
solution
(B) alternative
solution
(C) no
feasible solution at all
(D) no bounded
solution at all
Answer: C
02.
Given the problem to maximize
f(x), X = (x1, x2,......xn)
subject to m number of inequality constraints.
gi(x) ≤ bi, i = 1, 2......m
including the non-negativity constraints x ≥ 0.
Which of the following conditions is a Kuhn-Tucker necessary
condition for a local maxima at x̄ ?
(A) ∂L( X̄, λ̄
, S̄) / ∂xj = 0, j = 1, 2….m
(B) λ̄i [gi
(X̄) – bi]= 0, i = 1, 2 ….m
(C) gi (X̄) ≤
bi, i = 1, 2 ….m
(D) All of
these
Answer: D
03.
The following Linear Programming problem has :
Max Z = x1 + x2
Subject to x1 – x2 ≥ 0
3x1 – x2 ≤ –3 and x1, x2 ≥ 0
(A) Feasible
solution
(B) No
feasible solution
(C) Unbounded
solution
(D) Single
point as solution
Answer: B
04.
Given a flow graph with 10 nodes, 13 edges and one connected
components, the number of regions and the number of predicate (decision) nodes
in the flow graph will be
(A) 4, 5
(B) 5, 4
(C) 3, 1
(D) 13, 8
Answer: B
05.
Function points can be calculated by
(A) UFP ∗
CAF
(B) UFP ∗ FAC
(C) UFP ∗ Cost
(D) UFP ∗ Productivity
Answer: A
06.
Match the following :
List – I List – II
a. Data
coupling i. Module A and Module B have shared data
b. Stamp
coupling ii. Dependency between modules is based on the fact they
communicate by only passing of data
c. Common
coupling iii. When complete data structure is
passed from one module to another
d. Content
coupling iv. When the control is passed from one
module to the middle of another
a b c d
(A) iii ii i iv
(B) ii iii i iv
(C) ii iii iv i
(D) iii ii iv i
Answer: B
07.
A process which defines a series of tasks that have the
following four primary objectives is known a
1 to
identify all items that collectively define the software configuration.
2 to
manage changes to one or more of these items.
3 to
facilitate the construction of different versions of an application.
4 to
ensure that software quality is maintained as the configuration evolves over
time.
(A) Software
Quality Management Process
(B) Software
Configuration Management Process
(C) Software
Version Management Process
(D) Software
Change Management Process
Answer: B
08.
One weakness of boundary value analysis and equivalence
partitioning i
(A) they are
not effective.
(B) they do
not explore combinations of input circumstances.
(C) they
explore combinations of input circumstances.
(D) none of
the above.
Answer: B
09.
Which once of the following is not a software myth ?
(A) Once we
write the program and get it to work, our job is done.
(B) Project
requirements continually change, but change can be easily accommodated because
software is flexible.
(C) If we get
behind schedule, we can add more programmers and catch up.
(D) If an
organization does not understand how to control software projects internally,
it will invariably struggle when it outsources software projects.
Answer: D
10.
Match the following with respect to relationship between
objects and classes :
List – I List – II
a. State
diagram i. Useful for both abstract modelling and for designing
actual program
b. Object
diagram ii. Describes object classes
c. Class
diagram iii. Useful for documenting test cases
d. Instance
diagram iv. Describing the behaviour of a single
class of objects.
a b c d
(A) iv i ii iii
(B) ii iii iv i
(C) iii iv ii i
(D) ii iv i iii
Answer: A
11.
Match the following style rules for reusability :
List – I List – II
a. Keep
methods coherent i. Write a method to get the last
element of a list
b. Keep
methods small ii. Maintain parallel structure when
possible
c. Keep
methods consistent iii. Breaking a method into smaller parts
d. Provide
uniform coverage iv. Performs a single function or a group
of closely related functions.
a b c d
(A) iv iii ii i
(B) ii i iv iii
(C) iii iv ii i
(D) ii iii iv i
Answer: A
12.
Which is the protocol for performing RPCs between
applications in a language and system independent way ?
(A) Hyper Text
Transmission Protocol (HTTP)
(B) Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
(C) Simple
Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
(D) Simple
Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Answer: C
13.
The document that is used by XSLT to indicate, how to
transform the elements of the XML document to another format i
(A) HTML page
(B) DOC type
procedure
(C) Style
sheet
(D) Stored
procedure
Answer: C
14.
Which of the following concepts means adding new concepts to
a program as it runs ?
(A) Data
hiding
(B) Dynamic
loading
(C) Dynamic
typing
(D) Dynamic
binding
Answer: B
15.
Which of the following correctly describes overloading of
functions ?
(A) Virtual
polymorphism
(B) Transient
polymorphism
(C) Ad-hoc
polymorphism
(D) Pseudo
polymorphism
Answer: C
16.
Match the following with respect to programming languages :
List – I List – II
a. Structured
Language i. JAVA
b. Non-structured
Language ii. BASIC
c. Object
Oriented Programming Language iii. PASCAL
d. Interpreted
Programming Language iv. FORTRAN
a b c d
(A) iii iv i ii
(B) iv iii ii i
(C) ii iv i iii
(D) ii iii iv i
Answer: A
17.
The compiler converts all operands upto the type of the
largest operand is called
(A) Type
Promotion
(B) Type
Evaluation
(C) Type
Conversion
(D) Type
Declaration
Answer: A
18.
C++ actually supports the following two complete dynamic
systems :
(A) One
defined by C++ and the other not defined by C.
(B) One
defined by C and one specific to C++
(C) Both are
specific to C++
(D) Both of
them are improvements of C
Answer: B
19.
Important advantage of using new and delete operators in C++
i
(A) Allocation
of memory
(B) Frees the
memory previously allocated
(C) Initialization
of memory easily
(D) Allocation
of memory and frees the memory previously allocated.
Answer: D
20.
Match the following control strategies of prolog :
List – I List – II
a. Forward
movement i. Variable can be done with a constant, another variable
or a function.
b. Unification ii. The
entire conjunctive goal is executed.
c. Deep
backtracking iii. Previous sub goal to find
alternative solutions.
d. Shallow
backtracking iv. Chooses sub goal with possible
unifier.
a b c d
(A) iv i ii iii
(B) ii iv i iii
(C) iii i iv ii
(D) ii iii iv i
Answer: A
21.
Given the following statements :
S1: The
grammars S → asb | bsa | ss | a
and S → asb | bsa | a are
not equivalent.
S2: The
grammars S → ss | sss | asb | bsa | λ
and S → ss | asb | bsa | λ
are equivalent.
Which of the following is true ?
(A) S1 is
correct and S2 is not correct.
(B) Both S1
and S2 are correct.
(C) S1 is not
correct and S2 is correct.
(D) Both S1
and S2 are not correct.
Answer: A
22.
What are the final values of Q1 and Q0 after 4 clock cycles,
if initial values are 00 in the sequential circuit shown below :
(A) 11
(B) 10
(C) 01
(D) 00
Answer: D
23. High level
knowledge which relates to the use of sentences in different contexts and how
the context affect the meaning of the sentences ?
(A) Morphological
(B) Syntactic
(C) Semantic
(D) Pragmatic
Answer: D
24.
The objective of ___ procedure is to discover at least one
___ that causes two literals to match.
(A) unification,
validation
(B) unification,
substitution
(C) substitution,
unification
(D) minimax,
maximum
Answer: B
25.
If h* represents an estimate of the cost of getting from the
current node N to the goal node and h represents actual cost of getting from
the current node to the goal node, then A* algorithm gives an optimal solution
if
(A) h* is
equal to h
(B) h*
overestimates h
(C) h*
underestimates h
(D) none of
these
Answer: C
26.
The mean-end analysis process centers around the detection
of differences between the current state and goal state. Once such a difference
is isolated, an operator that can reduce the difference must be found. But
perhaps that operator can not be applied to the current state. So a sub-problem
of getting to a state in which it can be applied is set up. The kind of
backward chaining in which operators are selected and then sub goals are set up
to establish the precondition of operators is called
(A) backward
planning
(B) goal stack
planning
(C) operator
subgoaling
(D) operator
overloading
Answer: C
27.
In alpha-beta pruning, ___ is used to cut off the search at
maximizing level only and ___ is used to cut off the search at minimizing level
only.
(A) alpha,
beta
(B) beta,
alpha
(C) alpha,
alpha
(D) beta, beta
Answer: B
28.
If A and B are two fuzzy sets with membership functions
μA(x) = {0.2, 0.5, 0.6, 0.1, 0.9}
μB(x) = {0.1, 0.5, 0.2, 0.7, 0.8}
Then the value of μA ∩ B will be
(A) {0.2, 0.5,
0.6, 0.7, 0.9}
(B) {0.2, 0.5,
0.2, 0.1, 0.8}
(C) {0.1, 0.5,
0.6, 0.1, 0.8}
(D) {0.1, 0.5,
0.2, 0.1, 0.8}
Answer: D
29.
The height h(A) of a fuzzy set A is defined as
h(A) = sup A(x)
x ∈ A
Then the fuzzy set A is called normal when
(A) h(A) = 0
(B) h(A) <
0
(C) h(A) = 1
(D) h(A) <
1
Answer: C
30.
An artificial neuron receives n inputs x1, x2,...., xn with
weights w1, w2,...., wn attached to the input links.
The weighted sum ___ is computed to be passed on to a
non-linear filter φ called activation function to release the output.
(A) Σ wi
(B) Σ xi
(C) Σ wi + Σ
xi
(D) Σ wi ⋅ xi
Answer: D
31.
Consider the formula in image processing
RD = 1 – 1/CR
Where CR = n1 / n2
CR is called as compression ratio n1 and n2 denotes the
number of information carrying units in two datasets that represent the same
information. In this situation RD is called as relative ___ of the first data
set.
(A) Data
Compression
(B) Data
Redundancy
(C) Data
Relation
(D) Data
Representation
Answer: B
32.
Find the false statement :
(A) In Modern
Cryptography, symmetric key algorithms use same key both for Encryption and
Decryption.
(B) The
symmetric cipher DES (Data Encryption Standard) was widely used in the industry
for security product.
(C) The AES
(Advanced Encryption Standard) cryptosystem allows variable key lengths of size
56 bits and 124 bits.
(D) Public key
algorithms use two different keys for Encryption and Decryption.
Answer: C
33.
The message 11001001 is to be transmitted using the CRC
polynomial x3 + 1 to protect it from errors. The message that should be
transmitted i
(A) 110010011001
(B) 11001001
(C) 110010011001001
(D) 11001001011
Answer: D
34.
___ comparisons are necessary in the worst case to find both
the maximum and minimum of n numbers.
(A) 2n – 2
(B) n + floor
(lg n) – 2
(C) floor
(3n/2) – 2
(D) 2 * lg n –
2
Answer: C
35.
Let A and B be two n × n matrices. The efficient algorithm
to multiply the two matrices has the time complexity
(A) O(n3)
(B) O(n2.81)
(C) O(n2.67)
(D) O(n2)
Answer: B
36.
The recurrence relation T(n) = m T( n/2) tan2 is satisfied
by
(A) O(n2)
(B) O(nlg m)
(C) O(n2 * lg
n)
(D) O(n * lg
n)
Answer: *
37.
The longest common subsequence of the sequences X = <A,
B, C, B, D, A, B> and Y = <B, D, C, A, B, A> has length
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Answer: C
38.
Assuming there are n keys and each key is in the range [0, m
– 1]. The run time of bucket sort i
(A) O(n)
(B) O(n * lg
n)
(C) O(n * lg
m)
(D) O(n + m)
Answer: D
39.
A ___ complete subgraph and a ___ subset of vertices of a
graph G = (V, E) are a clique and a vertex cover respectively.
(A) minimal,
maximal
(B) minimal,
minimal
(C) maximal,
maximal
(D) maximal,
minimal
Answer: D
40.
Pumping lemma for context-free languages states :
Let L be an infinite context free language. Then there
exists some positive integer m such that any w ∈ L with |w|
≥ m can be decomposed as w = uv xy Z with |vxy| ___ and |vy| ___ such that uvż
xyż
Z ∈ L for all
ż = 0, 1, 2, ....... .
(A) ≤ m, ≤ 1
(B) ≤ m, ≥ 1
(C) ≥ m, ≤ 1
(D) ≥ m, ≥ 1
Answer: B
41.
The Greibach normal form grammar for the language
L = {an bn + 1 | n ≥ 0} i
(A) S → a SB,
B → bB | λ
(B) S → a SB,
B → bB | b
(C) S → a SB |
b, B → b
(D) S → a Sb |
b
Answer: C
42. Given the
following statements :
S1: Every
context-sensitive language L is recursive.
S2: There
exists a recursive language that is not context sensitive.
Which statement is correct ?
(A) S1 is not
correct and S2 is not correct.
(B) S1 is not
correct and S2 is correct.
(C) S1 is
correct and S2 is not correct.
(D) S1 is
correct and S2 is correct.
Answer: D
43.
What is the bit rate for transmitting uncompressed 800 × 600
pixel colour frames with 8 bits/pixel at 40 frames/second ?
(A) 2.4 Mbps
(B) 15.36 Mbps
(C) 153.6 Mbps
(D) 1536 Mbps
Answer: C
44.
In IPV 4, the IP address 200.200.200.200 belongs to
(A) Class A
(B) Class B
(C) Class C
(D) Class D
Answer: C
45. Which
layer of OSI reference model is responsible for decomposition of messages and
generation of sequence numbers to ensure correct re-composition from end to end
of the network ?
(A) Physical
(B) Data-link
(C) Transport
(D) Application
Answer: C
46.
A
client-server system uses a satellite network, with the satellite at a height
of 40,000 kms.
What is the best-case delay in response to a request ?
(Note that the speed of light in air is 3,00,000 km/second).
(A) 133.33 m
sec
(B) 266.67 m
sec
(C) 400.00 m
sec
(D) 533.33 m
sec
Answer: D
47.
The start and stop bits are used in serial communication for
(A) error
detection
(B) error
correction
(C) synchronization
(D) slowing
down the communication
Answer: C
48.
___ is a type of transmission impairment in which the signal
looses strength due to the resistance of the transmission medium.
(A) Attenuation
(B) Distortion
(C) Noise
(D) Decibel
Answer: A
49.
Match the following :
List – I List – II
a. Indexed
Addressing i. is not used when an operand is moved from memory into a
register or from a register to memory.
b. Direct
Addressing ii. Memory address is computed by
adding up two registers plus an (optional) offset.
c. Register
Addressing iii. Addressing memory by giving a
register plus a content offset.
d. Base-Indexed
Addressing iv. can only be used to access global
variables whose address is known at compile time.
a b c d
(A) ii i iv iii
(B) ii iv i iii
(C) iii iv i ii
(D) iii i iv ii
Answer: C
50.
Which of the following is a design criteria for instruction
formats ?
(A) The size
of instructions
(B) The number
of bits in the address fields
(C) The
sufficient space in the instruction format to express all the operations
desired.
(D) All of
these
Answer: D
51.
Synchronization is achieved by a timing device called a ___
which generates a periodic train of ___.
(A) clock
generator, clock pulse
(B) master
generator, clock pulse
(C) generator,
clock
(D) master
clock generator, clock pulse
Answer: A or D
52.
Serial access memories are useful in applications where
(A) Data
consists of numbers
(B) Short
access time is required
(C) Each
stored word is processed differently.
(D) None of
these
Answer: D
53.
What will be the output of the following logic diagram ?
(A) x OR y
(B) x AND y
(C) x XOR y
(D) x XNOR y
Answer: C
54.
The essential difference between traps and interrupts is
(A) traps are
asynchronous and interrupts are synchronous with the program.
(B) traps are
synchronous and interrupts are asynchronous with the program.
(C) traps are
synchronous and interrupts are asynchronous with the I/O devices.
(D) None of
these.
Answer: B
55.
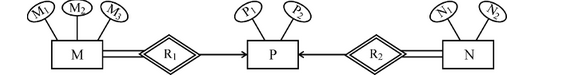
Consider the following ER diagram :
The minimum number of tables required to represent M, N, P,
R1, R2 is
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Answer: A
56.
Consider the following schemas :
Branch = (Branch-name, Assets, Branch-city)
Customer = (Customer-name, Bank name, Customer-city)
Borrow = (Branch-name, loan number, customer account-number)
Deposit = (Branch-name, Accountnumber, Customer-name,
Balance)
Using relational Algebra, the Query that finds customers who
have balance more than 10,000 is ___
(A) π
customer-name (σ balance > 10000 (Deposit)
(B) σ customer-name
(σ balance > 10000 (Deposit)
(C) π
customer-name (σ balance > 10000 (Borrow)
(D) σ
customer-name (π balance > 10000 (Borrow)
Answer: A
57.
Find the false statement :
(A) The
relationship construct known as the weak relationship type was defined by Dey,
Storey & Barron (1999)
(B) A weak
relationship occurs when two relationship types are linked by either Event-
Precedent sequence or Condition-Precedent sequence.
(C) Conceptual
model is not accurate representation of “Universe of interest”.
(D) Ternary,
Quaternary and Quintary relationships are shown through a series of application
scenario’s and vignette’s.
Answer: C
58.
Consider the table
Student (stuid, name, course, marks).
Which one of the following two queries is correct to find
the highest marks student in course 5 ?
Q.1. Select
S.stuid
From student S
Where not exists
(select ∗ from
student e
where e course = ‘5’ and e marks ≥ s marks)
Q.2. Select
s.stu.id From student S
Where s ⋅ marks >
any
(select distinct marks from student S
where s.course = 5)
(A) Q. 1
(B) Q. 2
(C) Both Q. 1
and Q. 2
(D) Neither Q.
1 nor Q. 2
Answer: B
59.
Armstrong (1974) proposed systematic approach to derive
functional dependencies. Match the following w.r.t. functional dependencies :
List – I List – II
a. Decomposition
rule i. If X → Y and Z → W
then {X, Z} → {Y, W}
b. Union
rule ii. If X → Y and {Y, W}→ Z
then {X, W} → Z
c. Composition
rule iii. If X → Y and X→ Z
then X → {Y, Z}
d. Pseudo
transitivity rule iv. If X → {Y, Z}
then X → Y and X → Z
a b c d
(A) iii ii iv i
(B) i iii iv ii
(C) ii i iii iv
(D) iv iii i ii
Answer: D
60.
Match the following :
List – I List – II
a. Secondary
Index i. Functional Dependency
b. Nonprocedural
Query Language ii. B-Tree
c. Closure
of set of Attributes iii. Relational Algebraic Operation
d. Natural
JOIN iv. Domain Calculus
a b c d
(A) i ii iv iii
(B) ii i iv iii
(C) i iii iv ii
(D) ii iv i iii
Answer: D
61.
Which of the following is not true with respect to a
trackball and/or spaceball ?
I. A
trackball is a two dimensional positioning device while as a spaceball provides
six degrees of freedom.
II. Unlike
the trackball a spaceball does not actually move.
III. A
trackball is a three dimensional positioning device while as a spaceball provides
six degrees of freedom.
(A) I & II
(B) II &
III
(C) II only
(D) III only
Answer: D
62.
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true ?
I. Two
successive translations are additive.
II. Two
successive rotations are additive.
III. Two
successive scaling operations are multiplicative.
(A) I and II
(B) I and III
(C) II and III
(D) All the
above
Answer: D
63.
Given below are three basic rules :
I. Squash
and Stretch
II. Slow-in
and Slow-out
III. To stage
the action properly
These rules are applied in case of
(A) (3, 0)
(B) (1, 0)
(C) (0.5, 0.5)
(D) (0.5, 0)
Answer: C
64.
Which of the following points lies on the same side as the
origin, with reference to the line 3x + 7y = 2 ?
(A) (3, 0)
(B) (1, 0)
(C) (0.5, 0.5)
(D) (0.5, 0)
Answer: D
65.
The transformation matrix required for conversion of CMY
colour model to RGB colour model is given as :
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Answer: C
66.
What steps shall be required to rotate an object about the
point P1 (as shown in fig. 1) and its placement such that what was at P1 is now
reduced and is at P2 (as shown in fig. 2) ?
I. Translate
P1 to origin
II. Scale as
required
III. Rotate
V. Translate
to the final position P2
(A) I, II and
III
(B) II, III
and IV
(C) I, III
& IV
(D) All of the
above
Answer: *
67.
In Unix, how do you check that two given strings a and b are
equal ?
(A) test $a
–eq $b
(B) test $a
–equal $b
(C) test $a =
$b
(D) Sh –C test
$a = = $b
Answer: C
68.
In windows 2000 operating system all the processor-dependent
code is isolated in a dynamic link library called
(A) NTFS file
system
(B) Hardware
abstraction layer
(C) Microkernel
(D) Process
Manager
Answer: B
69.
To place a sound into a word document, following feature of
windows is used :
(A) Clip board
(B) Task
switching
(C) C Win App
(D) OLE
Answer: D
70.
Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB) is
(A) a
cache-memory in which item to be searched is compared one-by-one with the keys.
(B) a
cache-memory in which item to be searched is compared with all the keys
simultaneously.
(C) an
associative memory in which item to be searched is compared one-by-one with the
keys.
(D) an
associative memory in which item to be searched is compared with all the keys
simultaneously.
Answer: D
71.
Simplest way of deadlock recovery is
(A) Roll back
(B) Preempt
resource
(C) Lock one
of the processes
(D) Kill one
of the processes
Answer: D
72.
The directory structure used in Unix file system is called
(A) Hierarchical
directory
(B) Tree
structured directory
(C) Directed
acyclic graph
(D) Graph
structured directory
Answer: C
73.
Which statement is not true about process O in the Unix operating
system ?
(A) Process O
is called init process.
(B) Process O
is not created by fork system call.
(C) After
forking process 1, process O becomes swapper process.
(D) Process O
is a special process created when system boots.
Answer: A
74.
Which of the following commands would return process_id of
sleep command ?
(A) Sleep 1
and echo $?
(B) Sleep 1
and echo $#
(C) Sleep 1
and echo $×
(D) Sleep 1
and echo $!
Answer: D
75.
Possible thread states in Windows 2000 operating system
(A) Ready,
running and waiting
(B) Ready,
standby, running, waiting, transition and terminated
(C) Ready,
running, waiting, transition and terminated
(D) Standby,
running, transition and terminated
Answer: B










0 comments:
Post a Comment
North India Campus