B.A., B.Sc. (General) 1st Semester Examination
Chemistry-Organic Chemistry-A
(Same for B.Sc. Microbial and Food Tech.)
Paper: II
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks: 22
Note: - Attempt five questions in all selecting one question from each Unit. Question No. 9 is compulsory. All questions carry equal marks.
Download Chemistry-Organic Chemistry-A Paper PDF file
Unit-I
1. (a) With the help of suitable examples, describe the effect of lone pairs of electrons on the central atom of a molecule on the bond angle of that compound.
(b) Define resonance effect. Account for the low reactivity of vinyl and aryl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions as compared to
(c) Define Hydrogen bonding. Explain why 2-hydroxybenzoic acid is 17 times stronger an acid compared to benzoic acid?
2. (a) What are free radicals ? Arrange the following radicals in order of increasing stability and explain the reason for your choice:
(CH3)2 CH, (CH3)3 Ċ, CH3, CH3 CH2
(b) What are rearrangement reactions? Discuss the role of [1, 2]-hydride and [1, 2]-methyl shifts in the rearrangement of carbocations ?
(c) Draw and explain the energy profile diagram of a non-concerted reaction with an isolable intermediate.
Unit-II
3. (a) Give the mechanistic details of Corey-House reaction for preparation of n-peptane.
(b) Write a note on sulphonation of alkanes.
(c) As the Kolbe's electrolysis reaction proceeds, the pH of solution gradually increases. Explain.
4. (a) Give details of the relative reactivity and orientation in halogenations of alkanes.
(b) Write a note on Dieckmann condensation reaction for the preparation of cycloalkanes.
(c) Describe the salient features of Baeyer's strain theory. Calculate the angle strain in a simple cyclopentane ring.
Unit-III
5. (a) With the help of suitable examples, explain the following :
(i) Ring-chain isomerism
(ii) Optical activity
(iii) Meso compounds
(b) Write notes on the following:
(i) Relative and absolute configurations
(ii) Alternating axis of symmetry
6. (a) Differentiate between the following, giving suitable examples :
(i) Internal and external compensation
(ii) Enantiomers and diastereomers
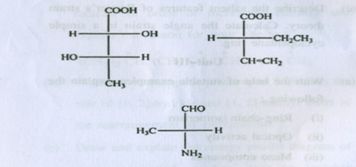
(b) Assign R or S configuration to the chiral centres in the following compounds:
(i) Substitution at equatorial position of cyclohexane is more stable that at axial position.
(ii) Twist boat conformation of cyclcohexane is more stable than the boat conformation.
(iii) trans-1, 2-Dichlorocyclopropane is optically active while cis-1, 2-dichlorocyclopropane is optically inactive. (Compulsory Question)










0 comments:
Post a Comment
North India Campus